

When designing an algorithm, consider if there is more than one way of solving the problem.
When designing an algorithm there are two main areas to look at:
Before an algorithm can be designed, it is important to check that the problem is completely understood. There are a number of basic things to know in order to really understand the problem:
Once these basic things are understood, it is time to design the algorithm.
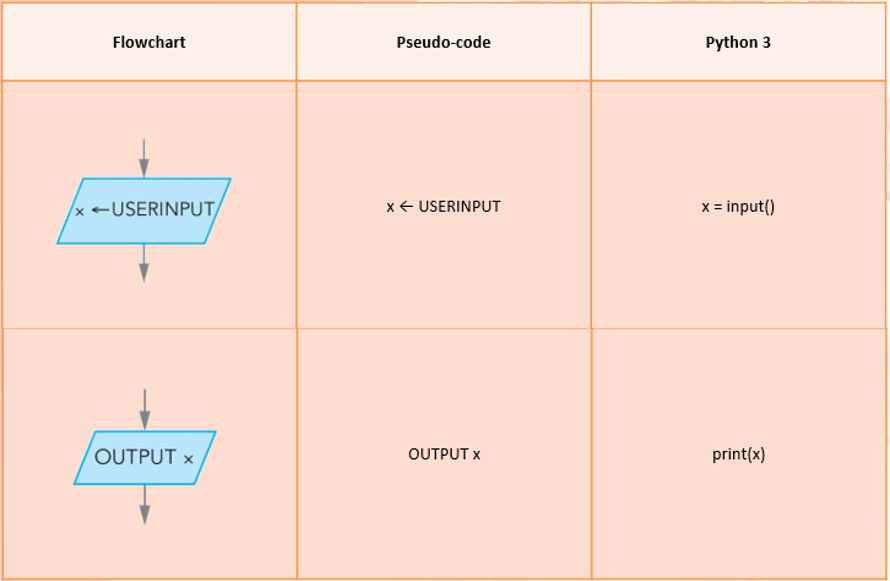
Most programs are developed using programming languages. These languages have specific syntax that must be used so that the program will run properly. Pseudocode is not a programming language, it is a simple way of describing a set of instructions that does not have to use specific syntax. Common pseudocode notation
There is no strict set of standard notations for pseudocode, but some of the most widely recognised are:
INPUT - indicates a user will be inputting something OUTPUT - indicates that an output will appear on the screenWHILE - a loop (iteration that has a condition at the beginning)FOR - a counting loop (iteration)REPEAT - UNTIL - a loop (iteration) that has a condition at the end IF - THEN - ELSE - a decision (selection) in which a choice is madePseudocode can be used to plan out programs.


Write out an algorithm in pseudo-code to ask a user to input three numbers and ouput the numbers in order of largest to smallest.
Write out a flowchart for a program that plays rock, paper, scissors: